Gout is an ancient disease that is caused by the overproduction or underexcretion of uric acid and leads to deposition of monosodium urate crystals in joints or other tissue. People who have serum uric acid concentrations above 7 mg per dL (420 μmol per L) may likely be precipitated in the synovial fluid. This disease is commonly affecting men than women.
Gout will show clinical manifestations that are divided into two which are acute and chronic arthritis. Acute gout is commonly presented as self-limiting that lasts from a few days to 2-3 weeks. There may be redness, extreme tenderness and swelling over the most affected joints which are the first metatarsal joint or your big toe, ankle joint, and finger joint. This disease usually attacks the single joint and lower limb is more likely to be affected.
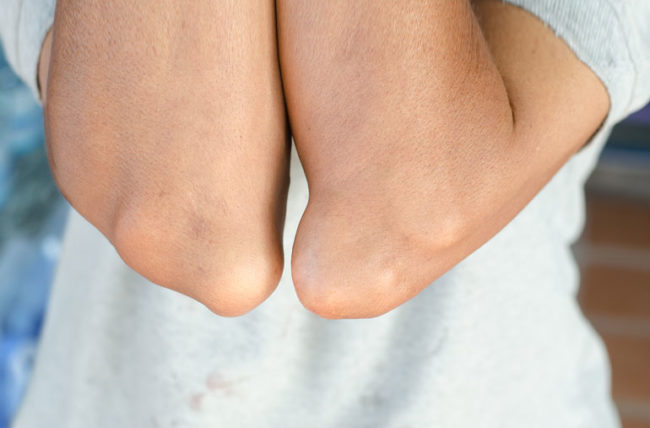
Chronic gout is marked by the formation of tophi which is a chalky deposit of monosodium urate and it involves many sites including digits of hands and feet, pinna of the ear, around the elbow or knee and achilles tendon. The presentations of chronic gout are usually painless swelling that appears firm and nodular in character. This toohi formation is usually correlated with elevated the severity of hyperuricemia which serum urate level exceeds 9 mg/dL.
Other than those mentioned above, gout can cause interstitial renal disease and uric acid nephrolithiasis or known as kidney stone if the monosodium urate deposits at the kidney. Thus, to avoid kidney failure, patients need to optimize the treatment in order to reduce the utare level in their body. Gout will be diagnosed if the patient fulfilled the two of four criteria:
- History of at least two attacks of painful joint swelling that resolves within 2 weeks
- The disease involving the big toe
- Presence of tophus
- The rapid response towards colchicine within 48 hours.
Gout treatment in Malaysia is also divided into two. In acute attacks, the goal of treatment is reducing pain and underlying inflammation. The best choice is NSAID, however, if the patient has peptic ulcer disease, it can be changed to a COX -2 inhibitor. Colchicine is an alternative drug if both drugs is contraindicated in patients with renal impairment, cardiac failure and hypertension.
In chronic gout, hypouricemic therapy is used to prevent recurrent attacks. In Malaysia, the commonly available drug is Allopurinol which is a xanthine oxidase inhibitor. However, this drug has life-threatening complications including rash, bone marrow suppression, hepatitis and jaundice if it is used with few medications. Thus, you need to inform your doctor if you are one of the users. Another choice is probenecid. Renal function needs to be monitored if you are using this drug.
Changing your lifestyle also can help to reduce uric acid in your body. You need to reduce weight since obesity can contribute to hyperuricemia. The goal is to achieve ideal weight, if weight loss is indicated, you can reduce weight gradually 0.5 to 1 kg per week. Restriction or elimination of alcohol since it can inhibit purine excretion. Reduced intake of purine-rich food such as red meat and seafood, instead consumption of low-fat dairy products is encouraged.
There is an option for surgery intervention which acts as the last resort. It is considered if the patient has chronic tophaceous gout which involves major joint destruction, loss of joint movements, pressure symptoms due to tophi collection, and tophaceous ulcer. Debridement is required if there is ulceration overlying tophi collection or if there is secondary infection. Frequent dressing is also required to heal the wound and avoid further complications such as bone infection and sepsis.